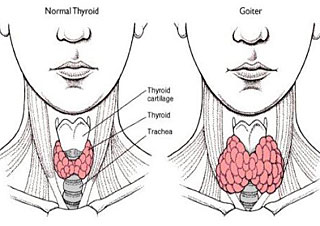
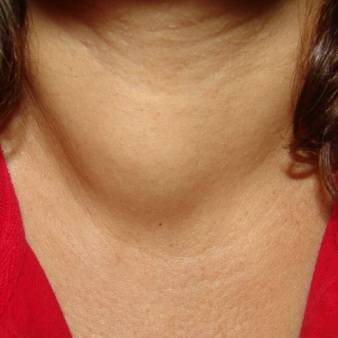
A simple goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is usually not cancer.
There are different kinds of goiters: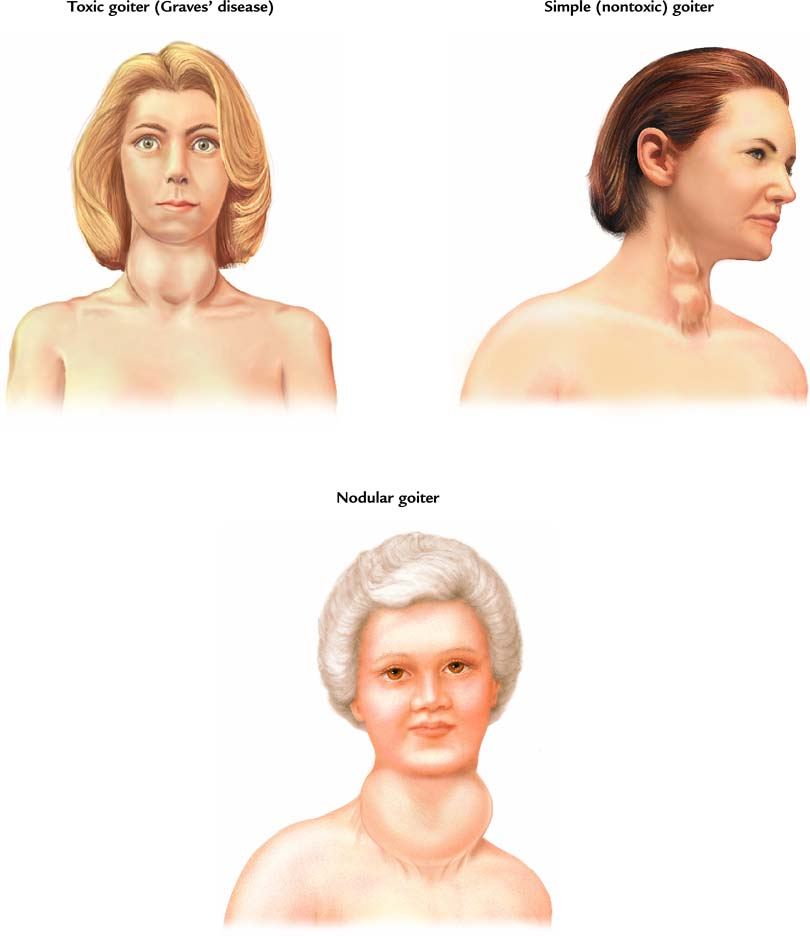
- A simple goiter can occur without a known reason. It can occur when the thyroid gland is not able to make enough thyroid hormone to meet the body’s needs. This can be due to a lack of iodine in a person’s diet. To make up for the shortage of thyroid hormone, the thyroid gland grows larger.
- Toxic nodular goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland that has one small, rounded growth (uninodular goiter) or many growths (multinodular goiter). The goiter is toxic if one or more of these nodules produce too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid).
- Multinodular goiter has multiple nodules. These can be either a:
- Toxic multinodular goiter makes too much thyroid hormone and causes hyperthyroidism) or overactive thyroid
- Non-toxic (does not make too much thyroid hormone).
It is not known what causes multinodular goiters in most cases, but iodine deficiency and certain genetic factors have been shown to lead to multinodular goiters.
The body needs iodine to produce thyroid hormone:
- Simple goiters may occur in people who do not get enough iodine in their diet.
- The use of iodized salt in many food products in the United States usually prevents a lack of iodine in the diet.
The cause of simple goiters is often unknown:
Factors other than iodine deficiency that may lead to the goiter include:
- Certain medicines (lithium, amiodarone)
- Infections
- Cigarette smoking
- Certain foods (soy, peanuts, vegetables in the broccoli and cabbage family)
Simple goiters are also more common in:
- Persons over age 40
- People with a family history of goiter

- Women
Symptoms:
The main symptom is an enlarged thyroid gland. The size may range from a single small nodule to a large neck lump.
Some people with a simple goiter may have symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism).
In rare cases, an enlarged thyroid can put pressure on the windpipe (trachea) and food tube (esophagus). This can lead to:
- Breathing difficulties (with very large goiters), especially when lying on the back
- Cough
- Hoarseness
- Swallowing difficulties, especially with solid food
Outlook (Prognosis)
A simple goiter may disappear on its own, or may become larger. Over time, the thyroid gland may stop making enough thyroid hormone. This condition is called hypothyroidism.
In some cases, a goiter becomes toxic and produces thyroid hormone on its own. This can cause high levels of thyroid hormone, a condition called hyperthyroidism.
Call your health care provider if you experience any swelling in the front of your neck or any other symptoms of goiter.
Prevention
Using iodized table salt prevents most simple goiters.
Alternative Names: Simple goiter; Endemic goiter; Colloidal goiter; Nontoxic goiter; Toxic nodular goiter